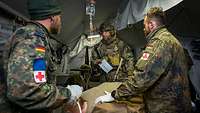
The Army Medical Service is a special-to-arm service of the German Army and only a small part of the Bundeswehr Medical Service. Its servicemen and women are thus counted among the combat service and command support forces. Their mission is generally identical to that of all Bundeswehr medical forces, namely to protect, maintain and restore the health of military personnel.
This applies especially to operations abroad, where particular health risks lie in wait. Military personnel who fall ill, have an accident or are wounded on operations abroad are expected to receive medical care that ultimately meets the professional standards applied in Germany. The mission of the Army Medical Service is geared to tasks in the context of international conflict prevention, crisis management, and national and collective defence, in which regard lessons learned from the various battle groups and task forces are at all times taken into account. It is with this in mind that the units of the Rapid Response Forces Division (Division Schnelle Kräfte - DSKDivision Schnelle Kräfte) also have their own (organic) airborne and airmobile medical forces at their disposal for routine medical support in Germany.
The Army also has organic flight medical teams for the aeromedical support of personnel during training, exercises and operational deployments. These teams provide both aeromedical care and medical emergency response services at Army airfields.
The Army Medical Service encompasses some 550 military personnel.
Technical Command and Control Structure
The Surgeon General of the Army has technical control over the Army Medical Service. He also represents the interests of the Army vis-à-vis the Surgeon General of the Bundeswehr, and vice versa.
Organisationally, the Surgeon General of the Army is located at the German Army Headquarters and directly advises the Army leadership on medical and Army Medical Service-related matters.
Technically, all corps and division surgeons, the Senior Flight Surgeon of the Army, and the command surgeon in Army Training Command report to the Surgeon General of the Army. He has disciplinary authority over the Army Medical Service personnel.
Medical Service at Headquarters
Medical command, control and advisory elements, corps, division and brigade surgeons, as well as senior medical officers and the command surgeon are assigned, structurally speaking, at subordinate command headquarters and at division and brigade level. Their core mission is to advise the commanders on all medical service matters. These senior physicians plan, manage, coordinate and supervise activities aimed at assuring medical readiness and medical support services.
Medical Service of the Rapid Response Forces Division
Army Medical Service forces are employed primarily in the Rapid Response Forces Division. To take account of the particular conditions under which the special operations forces and specialised forces operate, the two paratroop regiments (26 and 31) of 1 Airborne Brigade, and the Special Operations Forces Command, or SOFCOM (Kommando Spezialkräfte - KSKKommando Spezialkräfte), have organic medical forces at their disposal. This organic medical service is under the technical control of the division surgeon.
The airborne medical companies are fully jump-qualified, constituting an important and unique feature of these medical personnel.
The Special Operations Forces Command (KSKKommando Spezialkräfte) also has its own medical clinic to take account of its particular OPSEC needs. Being the only medical clinic not part of the Bundeswehr Joint Medical Service is a significant and unique feature, assuring that Special Operations Forces Command personnel receive qualified initial medical treatment and survive for onward evacuation and subsequent medical care by forces of the Bundeswehr Joint Medical Service.
Mechanised Divisions
The structure of the Army is rigorously geared to the “brigade system”. The brigade is the prime manoeuvre element for being able to cover the Army’s broad task spectrum and also for ensuring the inner cohesion of the field forces.
When in routine duty mode, the mechanised divisions do not have any organic medical forces and assets apart from division and brigade surgeons along with assigned support personnel as command, control and advisory elements. But when in training, on exercises and on operational deployments, they are supported by the Bundeswehr Joint Medical Service with the necessary medical capabilities.